How To Use Kt Tape For Lcl
Introduction:
Taping for lateral collateral ligament tear is near used technique to relive hurting and further support to the injured ligament.This is nearly effective and supportive treatment.It is give static as well as dynamic support to the injured knee.
kinesio taping give dynamic stability to the joint while typical taping give static stability to lateral collateral ligament injury. information technology is also called kinesiology tape or kinesiology therapeutic tape. is an elastic cotton strip with an acrylic adhesive that is purported to ease pain and disability from athletic injuries and a multifariousness of other physical disorders.
Taping on your knee can help stabilize it when you are active and can requite relief from pain.information technology is nearly popular technique. mostly use in sport injuries because during playing whatever sport knees are more prone to injured. information technology is because of sudden thrust on knees or twisting of the knee during the sport. the lateral collateral ligament also more pron to injured during road traffic accident.
Kinesiological tapping could exist a rehabilitative cum protecting apply of elastic kinesiological tapes to supply :
- reduction in genu pain whereas LCL abraded
- enhancing functioning of affected knee
- preventing any injuries to the knee
- back up to the articulatio genus joint
- repositioning of construction of human knee
- facial and ligamentous correction of knee.
- It facilitate the healing methodology whereas providing full computer memory with support to the joints suppotive structure yet equally mobilization effects.
- The lateral collateral ligament is a thin band of tissue running along the outside of the knee. Information technology connects the thighbone (femur) to the fibula, which is the small bone of the lower leg that runs down the side of the knee and connects to the ankle.is one of the major stabilizers of the knee joint joint with a primary purpose of preventing excess varus and posterior-lateral rotation of the human knee.
- Although less frequent than other ligament injuries, an injury to the lateral collateral ligament (LCL) of the genu is nigh ordinarily seen subsequently a high-energy accident to the anteromedial knee, combining hyperextension and farthermost varus force.
- The lateral collateral ligament tin can also exist injured with a not-contact varus stress or non contact hyperextension of knee. The lateral collateral ligament most usually occurs in sports (forty%) with high velocity pivoting and jumping such every bit soccer basketball, skiing, football game or hockey. Lawn tennis and gymnastics take been shown to have the highest likelihood of an isolated lateral collateral ligament injury.
- The lateral collateral ligament is rarely injured alone and therefore boosted damage of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), and posterior-lateral corner (PLC) is common along with the lateral collateral ligament when the lateral knee structures are injured.
Relevant Anatomy of LCL :
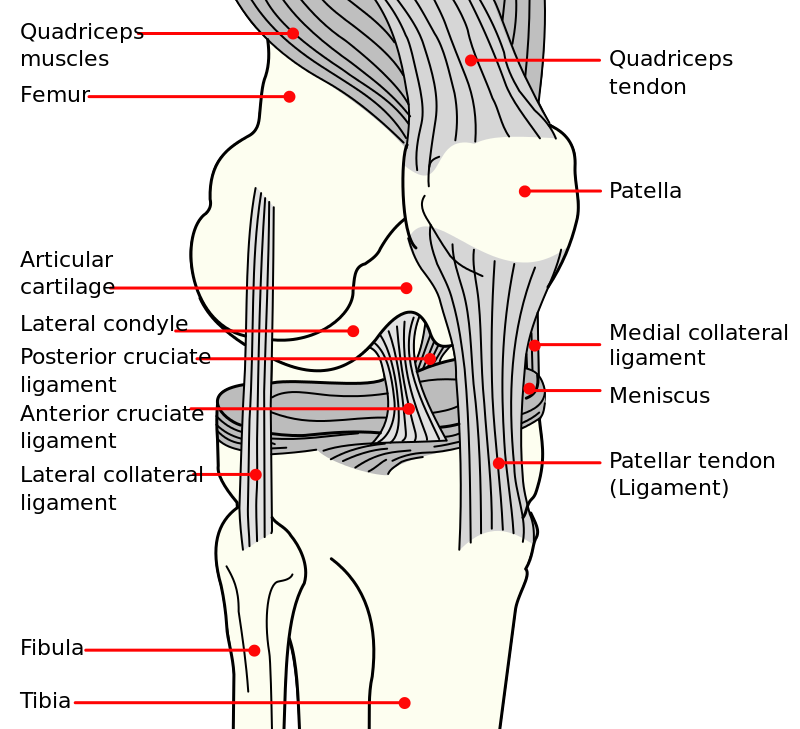
origin : posterior (3.one mm) and proximal (i.4 mm) to lateral epicondyle
posterior and proximal to origin of popliteus
popliteus origin is 18.v mm from lateral collateral ligament origin
insertion : anterolateral fibular head
covers 38% of the fibular width
most anterior structure on proximal fibula
lodge of insertion from anterior to posterior
LCL → popliteofibular ligament → biceps femoris
Blood supply : anterior tibial recurrent arteries and inferolateral geniculate arteries.
The lateral collateral ligament is a cord-like structure of the arcuate ligament circuitous, together with the biceps femoris tendon, popliteus muscle and tendon, popliteal meniscal and popliteal fibular ligaments, oblique popliteal, arcuate and fabellofibular ligaments and lateral gastrocnemius muscle.
The lateral collateral ligament is a stiff connectedness betwixt the lateral epicondyle of the femur and the head of the fibula, with the office to resist varus stress on the articulatio genus and tibial external rotation and thus a stabilizer of the human knee. When the knee joint is flexed to more than xxx°, the lateral collateral ligament is loose. The ligament is strained when the knee is in extension.
Causes of LCL tear:
- Lateral collateral ligament tears typically happen when y'all're playing a sport that involves:
- Angle.
- Hard contact.
- Quick changes of management.
- Twisting.
- Jumping.
- Weaving.
- Stop-and-go movements.
- The riskiest sports for LCL tears include:
- Football game.
- Skiing.
- Soccer.
Symptoms of LCL tear:
Astute :
- Patients with an acute lateral collateral ligament injury will present with a history of an acute incident which most normally consisted of a blow to the medial human knee while in full extension or extreme not contact varus bending of the genu. Pain, swelling and ecchymosis are oftentimes present at the lateral joint line along with difficulty in full weight bearing.
- Less common complaints consist of a thrust gait, pes boot during mid stance, paresthesia down the lateral lower extremity as well every bit weakness and/or pes drib.
- Upon evaluation, a patient with an acute lateral collateral ligament injury may nowadays with reduced range of motion, instability/giving way during weight bearing also weakness of the quadriceps (inability to perform a straight leg raise). The patient will present with pain likewise as increased carbs movement when performing a Varus Stress Test.
Sub-Astute:
- Patients who present with a sub-acute lateral collateral ligament injury will nowadays with lateral knee pain, stiffness with end of range flexion or extension of knee joint, overall weakness and possible instability/giving mode.
Chronic:
- Patients with a chronic lateral collateral ligament injury will present with unspecific genu hurting, meaning weakness throughout the entire kinetic concatenation as well as potential instability and mal-adaptive move patterns of genu.
Grades of LCL tear:
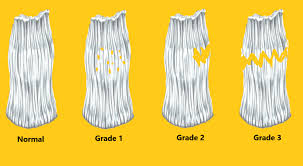
Grade ane: Knee joint injuries are balmy. Your lateral collateral ligament is not completely torn. You should heal with simply at habitation treatment every bit well equally the utilization of your crutches. Your healthcare provider might also have you wear a hinged knee brace when you are allowed to put some weight on your knee. You will likely experience better afterwards about three to iv weeks.
Grade iii: Knee injuries are severe. Your lateral collateral ligament is separated or torn completely and may take 8 to 12 weeks to heal. You will use a hinged brace for several months. Your healthcare supplier might recommend surgery.
Grade 2: Knee injuries are considered moderate. Yous accept a partial tear in your lateral collateral ligament. For a class 2 injury, you lot have need to use crutches so a hinged knee joint caryatid. Recovery will accept about viii to twelve weeks.
Special examination for LCL tear:
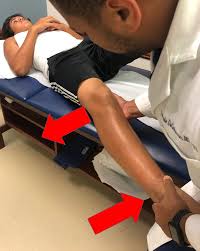
one-Varus Stress Test– The most assist full special test when assessing a LCL injury. With the femur stabilized, a varus force is practical with special attending to the lateral articulation line. The examination is first performed in 30 degrees flexion. Increased laxity or gaping is may exist an LCL injury with possible PLC involvement. Test is then performed with knee joint in full extension. Improved stability indicates an isolated LCL injury while continued gaping is a positive test for LCL and PLC injury.
2-External Rotation Recurvatum Test- With the patient in supine, a supra patellar forcefulness is applied while the great toe is used to lift and externally rotate the tibia. Excessive hyperextension when compared to the uninvolved limb is indicative of a positive test.
3-Posterolateral Drawer Exam- With the patient in prone, the knee is flexed to xc degrees and externally rotated xv degrees. The examiner and so provides a posterior strength to the femoral condyles. Excessive Posterolateral translation is a positive test and indicative of a PLC injury.
4-Reverse Pivot Shift- With the patient in prone, the examiner slowly extends the knee joint while providing a valgus and external rotating force. The examination is positive if a 'clunk' is felt at 30 degrees. Test must be performed bilaterally, as false-positives have been identified on the not-involved limb.
5-Dial Exam– With the patient in prone, the examiner stabilizes the femur while the lower limb is externally rotated. The test is performed bilaterally at 30 degrees and 90 degrees of articulatio genus flexion. Ten degrees or more of external rotation is a positive examination and indicative of a PLC injury.
Aim of LCL sprain taping:
- The aim of taping for a lateral collateral ligament sprain is to produce back up and protection to the injured ligament. The lateral collateral ligament is a narrow ligament which connects the femur (thigh bone) to the fibula on the outside of the articulatio genus.
- If the lateral collateral ligament is sprained, this propose it is stretched, partially torn or in rare cases completely ruptured. Support strips of tape are practical along the length of the injured ligament to 'reinforce' information technology. The back up strips help prevent sideways movement of the human knee joint or prevent further harm to genu joint, which would put stress on the lateral collateral ligament and as a effect prevent healing of lcl tear.
- If yous have had badly torn or stretched ligaments in the by and then lateral knee ligament taping provides actress support and stability to the knee joint,also prevent further harm of knee joint. in the same way a hinged knee brace give support every bit well as stability to human knee.
- Record provides a high level of support for a shorter menstruum of time. Record volition naturally stretch within the offset hour or two, depending on the demands yous identify on it. Then information technology should be re-practical.
Taping for LCL tear:
- Taping used in employed in the field of rehabilitation as a method of treatment for knee injuries but much of the show is contradictory.
- Taping is one amid the adjunct treatments that we have a trend to as physiotherapists would possibly employ with our patients together with well supported techniques like patient education and exercise therapy.
- we have a trend to could debate that if tape includes a positive impact, exist it placebo or mechanical, then nosotros must always use information technology.
- provides a firm support, holds and reduces motion of a joint with a powerful and gummy textile, examples include Strappal or Endura Fix.
- Rigid strapping tape normally used in tape or strapping is normally referred to as "sports tape" or "able-bodied record" and is almost frequently a rigid type of strapping record.
- Elastic husky tape may be used once less rigidity or support is needed.
- There are two blazon of taping for LCL tear i.Rigid taping 2.Kinesio taping .this two are given below with description.
ane.Rigid taping:
- Rigid strapping is most commonly practical before training, or a friction match, and is designed to stabilize a joint and support tendons and ligaments attachments. Muscle injuries and support is mostly improve treated with rigid tape, K-Tape or Cohesive record. Over-taping the joint and/or taping likewise oftentimes can sometimes lead to other injuries, as other joints and muscles can be forced to recoup for the dislocated area and information technology's lack of natural movement. Always seek professional medical communication for injuries.
- All tapes work best on dry and make clean skin surfaces. Avoid moisturizing the peel and very hairy skin as this will form a bulwark and adversely bear on the adhesive qualities of any tape. Rigid tape sticks better to itself than to pare, and so overlapping tapeon-tape, or fixing onto a record anchor works best. Rigid tape is non-stretchy. Try to handle and place the tape carefully to avert creasing the tape wherever possible.
Application:
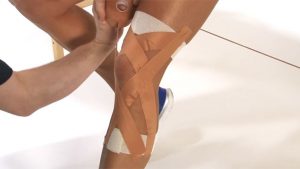
- 1- This taping example is a very symmetrical type of taping.Create an anchor record wrap with no tension 10cm above the knee.
- ii- Create an anchor wrap with no tension 10cm below the knee.
- 3- With two strip of rigid tape( cur long enough to reach from superlative to bottom anchor strip at an bending.) Create an 'X' shape.
- 4- Ballast points for the initial two strips of 'X' tape at the front and back of the knee and are onto the ballast wrap tapes.They are in line with the heart of the knee cap (12 O'clock for record strip.) The overlapping department of 'X' taping strips should be directly over the bony inside aspect of the knee joint.
- five- Continue creating more '10' taping strips within strip and in symmetrical style until they encounter in the middle . Ensure each strip of new 'X' tape applied is slightly over lapping the immediate previous strip placed.The crossover part of the 'X' always being placed directly over the bony lateral collateral ligament.
- 6- Using elastic agglutinative bandage now back up the rigid record by adding another layer of tape. Now follow the line of the very first strip of 'X' tape placed from height to bottom,crossing straight over the bony lateral collateral ligament.
- 7- Follow the lower anchor tape strapping effectually the leg one time or twice a small-scale amount of stretch.This is creating a figure viii of tape shape from superlative anchor to lower ballast around the thigh and shin.
- 8- Complete the last part of the rubberband adhesive bandage tape '10' from lower to upper leg.once again taping over the bony lateral collateral ligament. And then complete a final wrap in one case effectually the top thigh anchor wraps.With little stretch/pressure.Taping closer to the patella will back up genu cap further.
- 9- A final small strip of rigid tape can exist applied over the stop of the elastic adhesive bandage taping,if desired to agglutinative strength and assistance the tape from becoming unstuck due to friction or chafe.
2.Kinesio taping :
Kinesio Taping Method is a therapeutic tool utilised by the rehabilitation specialists in all programs (paediatric, geriatric, orthopaedic,neurological, oncology and others) and levels of care (acute care, inpatient rehabilitation, outpatient, abode care and Twenty-four hour period Rehab). The thought of using elastic record to mimic the therapist's hands was starting time presented past Dr Kenzo Kase in the 1970s.
Application :
Causes of outer knee pain may include It Ring Syndrome, overuse, over training, poor preparation grade, or training on hills or stairs. KT Tape relieves human knee pain and promotes the healing process.
What you demand :
2 strips of KT Tape
one full 25cm strip
1 total 25cm strip cut in half
Apply before action:
Use one hour before beginning activity
Make clean skin:
Clean clay, oils and lotions from surface area where nosotros apply tape .
Activate adhesive:
Afterwards application rub record vigorously to activate adhesive so effect is produce at that time.
Application :
Trunk position of the subject is setting or supine with articulatio genus at a 90 degree bend.
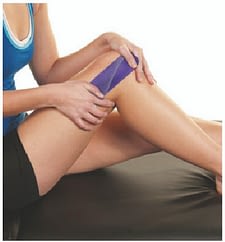
80% Stretch :
Anchor the centre of a half strip of tape over the betoken of pain with fourscore% stretch.
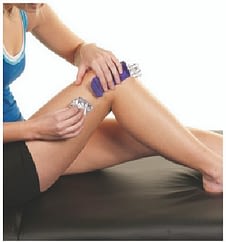
0% Stretch:
Lay ends down without stretch.
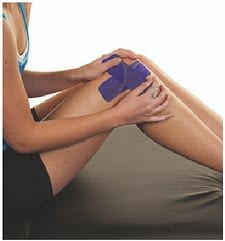
80% Stretch:
Anchor the middle of a second half strip in an X design over the first strip with 80% stretch
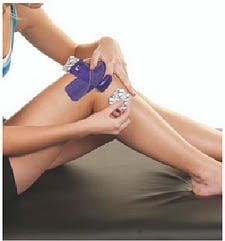
0% Stretch:
Apply ends of record without stretch.
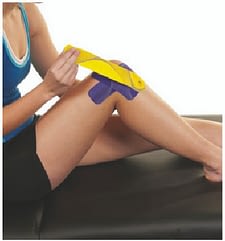
0% Stretch:
Anchor a full strip betwixt the lower ends of the Ten without stretch.
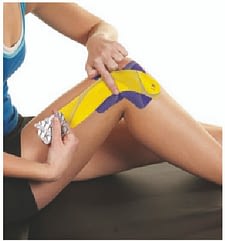
25% Stretch:
Use the record up the thigh as shown with 25% stretch.
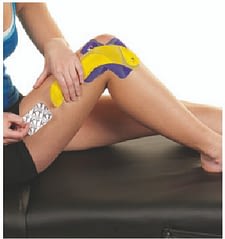
0% Stretch:
Apply the concluding 5cm of tape without stretch.
How to remove?
- So presently you've got your tape on and you've gotten that additional support throughout your called sporting activity, it'south time to need it off, and so enable the U.s. to ease the tactic of removing physiology tape for you. the foremost effective tip we are going to provide one time it involves removing your physiology tape is to peel the skin from the record, not the tape from the skin.
- But in terms of the bodily methodology, 1st ensure you're removing the tape in an equivalent management as a event of the expansion of the hair below information technology, and despite what y'all're doing don't rip the record off kind of a plaster!
- Start slowly, folding the corners of the sting dorsum fleck by bit, guaranteeing that you're nascence the removed tape on the rear of the practical tape, as opposition propulsion the record on top of and aloof from your arm.
- As yous're scraping the record, concur your skin downwards abreast your completely different paw and either regulator it or pull it gently among the contrary means of the record. This helps the peel and so the record to separate heaps expeditiously but with no discomfort.
- If the tape has been practical over a furred region of the body, it helps to maneuver on the tape as yous are peeling information technology off, as a issue of the force per unit area helps avoid a lot of hurting.
- It'south knowing have shaved the realm before applying the tape simply, equally this isn't ofttimes smart, taking this precaution square mensurate reaching to be necessary to some.
- want a fleck boosted aid? Apply oil directly onto the tape, rub information technology in and wait effectually 10 to twenty minutes earlier removing it slowly. This will facilitate reducing the viscousness of the tape and build it easier to induce obviate.
How To Use Kt Tape For Lcl,
Source: https://samarpanphysioclinic.com/taping-technique-for-lateral-collateral-ligament-tear/
Posted by: seaboltwiche1975.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Use Kt Tape For Lcl"
Post a Comment